Types of Gears Used for Robotics
In robotics, various types of gears are utilized to achieve precise control, efficient power transmission, and smooth operation. Each type of gear offers unique advantages, making them suitable for different robotic applications. Here’s a brief overview of the key gear types commonly used in robotics:
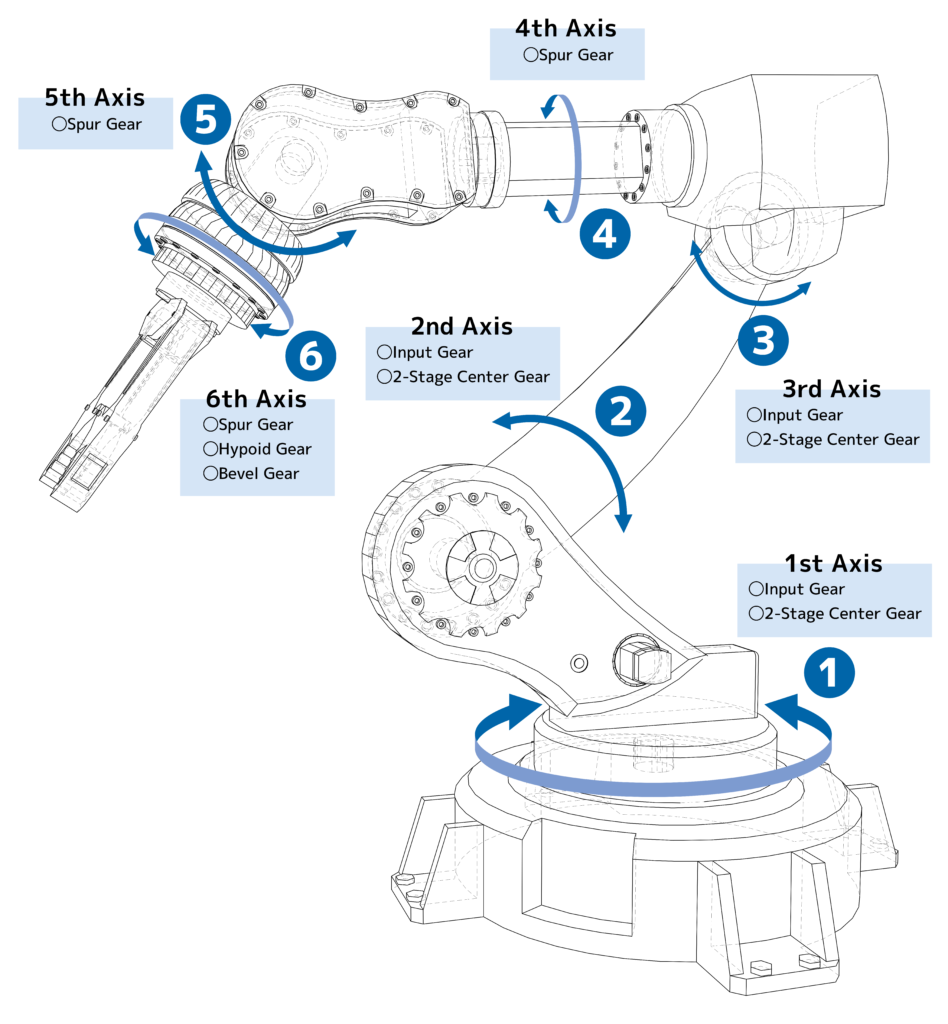
Bevel Gears
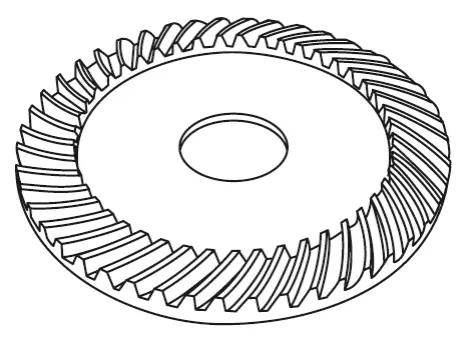
evel gears are used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. These gears are essential in robotics for applications requiring a change in the direction of motion, such as in robotic arms or joint mechanisms. Bevel gears are available in different forms, including straight, spiral, and hypoid, to accommodate various needs for smooth and efficient power transfer.
2-stage Center Gears
The 2-stage center gear setup is employed in robotics to achieve a higher gear reduction ratio within a compact space. This configuration uses two sets of gears to multiply the reduction ratio, providing greater torque and slower output speeds. It’s ideal for robotic applications where precise and controlled movement is necessary, such as in robotic grippers or wheel drives.
Hypoid Gears
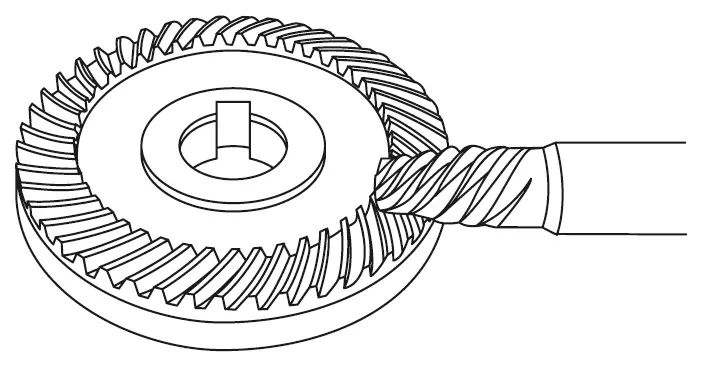
Hypoid gears are a type of bevel gear with an offset between the driving and driven shafts. This offset allows for smoother and quieter operation compared to standard bevel gears. Hypoid gears are often used in robotics where noise reduction is critical, and they provide efficient power transmission in applications like robotic legs or other moving joints.
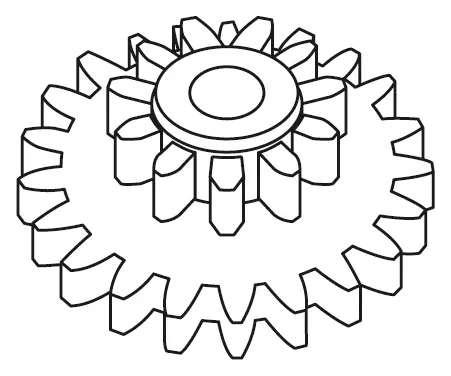
Spur Gears
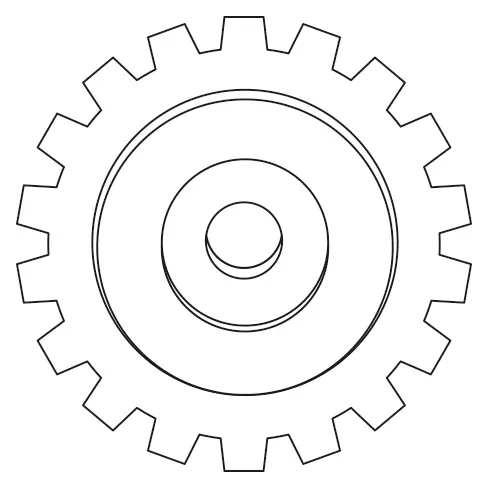
Spur gears are the most common type of gear used in robotics. These gears feature straight teeth and are used to transmit motion between parallel shafts. Spur gears are valued for their simplicity, reliability, and efficiency, making them ideal for a wide range of robotic applications, from basic movement mechanisms to complex gear trains.
Input Gears
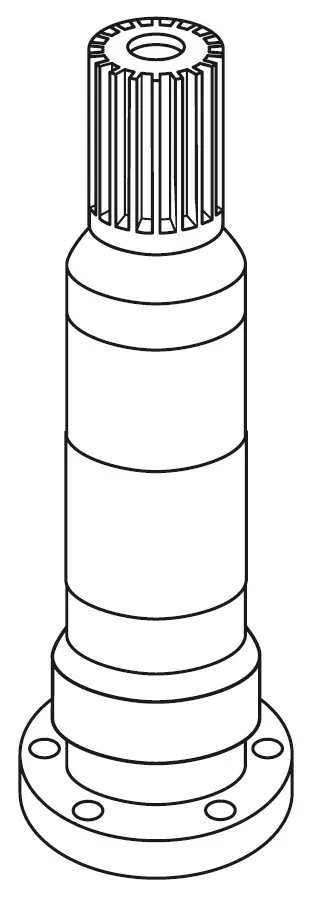
The input gear is the first gear in a gear train, responsible for receiving power from a motor or another source and transferring it to the subsequent gears in the system. In robotics, input gears are critical for initiating the gear train that drives various robotic components. The choice of input gear impacts the overall performance, speed, and torque of the robotic system.
Applications of Gears in Robotics
Industrial Robots

Industrial robots are heavily used in manufacturing environments for tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and material handling. These robots require precise and powerful movement, which is achieved through the use of gears such as bevel gears, spur gears, and hypoid gears. Gears are critical in industrial robots for transferring power from motors to the robot's arms and joints, enabling accurate positioning and smooth operation even under heavy loads. The durability and efficiency of these gears ensure that industrial robots can operate continuously in demanding environments with minimal maintenance.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)

Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human workers, assisting in tasks that require precision, safety, and flexibility. Gears in cobots, such as 2-stage center gears and spur gears, are essential for controlling the robot’s movements with high accuracy and low noise. The integration of these gears allows cobots to perform delicate tasks, such as assembling small parts or handling sensitive materials, while ensuring smooth and safe interaction with humans. The compact and efficient gear systems in cobots enable them to operate in tight spaces and adapt to various tasks with ease.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)

Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are designed to navigate and perform tasks independently within dynamic environments, such as warehouses or hospitals. Gears play a vital role in the mobility and maneuverability of AMRs. For example, bevel gears and input gears are used to control the direction and speed of the robot’s wheels or tracks. These gears enable precise steering and speed control, allowing AMRs to navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and perform tasks like transporting goods or delivering supplies efficiently.
Medical and Surgical Robots

Medical and surgical robots require an exceptional level of precision and control to perform delicate procedures. In these robots, gears such as hypoid gears and spur gears are used to achieve smooth, precise, and silent operation. These gears are crucial for controlling the movement of robotic arms and surgical instruments, ensuring that the robot can perform intricate tasks with minimal margin for error. The use of high-precision gears in medical and surgical robots also enhances their reliability and safety, making them indispensable tools in modern healthcare.
Key Considerations for Robot Gears
Gear Rotation Direction
In robotics, the direction of gear rotation is crucial, as robotic arms often move in various directions—up, down, left, and right—requiring both forward and reverse rotation. The sound produced by the gears can vary depending on whether they are rotating forward or in reverse, which can lead to changes in operational noise based on the robot's movement direction. To prevent this, it is essential to ensure that both the right and left gear tooth surfaces are finished with equal precision, maintaining consistent performance and sound quality regardless of rotation direction.
Minimizing Backlash
Minimizing backlash is vital for enhancing the positional accuracy of robotic arms. Excessive backlash can negatively impact the precision of the arm's movements. To improve positioning accuracy, it’s important to design mechanisms that minimize backlash and aim for tighter tolerance control on the gear tooth thickness. By doing so, the overall precision and performance of the robotic arm can be significantly enhanced.
High speed, compact size and design
Robotics demands gears that support high-speed operations while being compact and lightweight. Thin-walled designs are often required to achieve these goals, ensuring that the gears contribute to the robot's overall efficiency without adding unnecessary bulk. Additionally, design is a critical factor, as gears must be manufactured to fit within limited spaces while still meeting the functional and aesthetic requirements of the robot.
Proactive Development
When it comes to new product development, gears and other components are often required to be produced on very short lead times. While gears typically have longer production timelines, delays in the design phase can necessitate expedited manufacturing. This is especially true in years with trade shows, where there is an increased demand for rapid prototyping of robots intended for exhibition. Staying agile in the development process is key to meeting these demands and ensuring timely delivery of high-quality components.
Narutaki's Gear Manufacturing Service
What we offer
At Narutaki Industries, we specialize in providing custom solutions for your gear manufacturing needs. Whether you’re in the robotics, automotive, or consumer electronics industry, our expertise in precision bevel and miter gears ensures that you receive the highest quality products tailored to your specific requirements. We offer a wide range of materials, from durable plastics like POM and Nylon to advanced engineering plastics, to meet the demands of your application.
Product examples
Bevel/Miter Gear (Carbon Steel)

- Material: S45C (AISI 1045)
- Module: 1.5
- DP: 16.9
- Number of teeth: 48
- Helix angle: 35°
Bevel/Miter Gear (Alloy Steel, Module: 1.0)

- Material: SCM415(AISI 4115)
- Module: 1.0
- DP: 25.4
- Number of teeth: 10
- Helix angle: 35°
Bevel/Miter Gear (Alloy Steel, Module: 1.25)

- Material: SCM415(AISI 4115)
- Module: 1.25
- DP: 20.3
- Number of teeth: 38
- Helix angle: 35°
Bevel/Miter Gear (Alloy Steel, Module: 1.3)

- Material: SCM415(AISI 4115)
- Module: 1.3
- DP: 19.5
- Number of teeth: 21
- Helix angle: 35°
Bevel/Miter Gear (Alloy Steel, Module: 1.5)

- Material: SCM415(AISI 4115)
- Module: 1.5
- DP: 16.9
- Number of teeth: 21
- Helix angle: 35°
Bevel/Miter Gear (Alloy Steel, DP: 18)

- Material: SCM415(AISI 4115)
- DP: 18
- Number of teeth: 12
- Helix angle: 35°
Our team is dedicated to delivering gears that excel in performance, durability, and precision. From prototype development to full-scale production, we support you at every stage of the manufacturing process, ensuring that your project is completed on time and to your exact specifications.